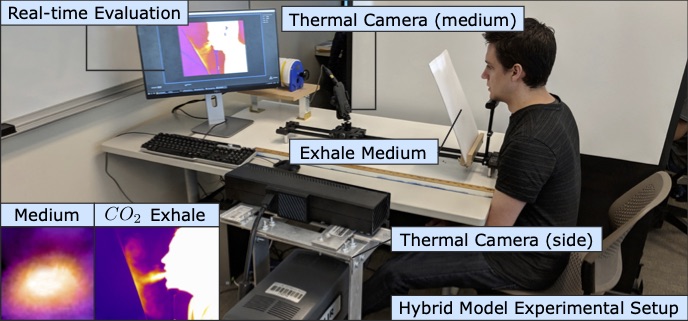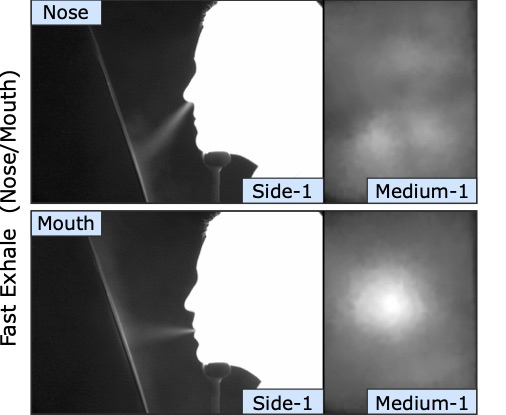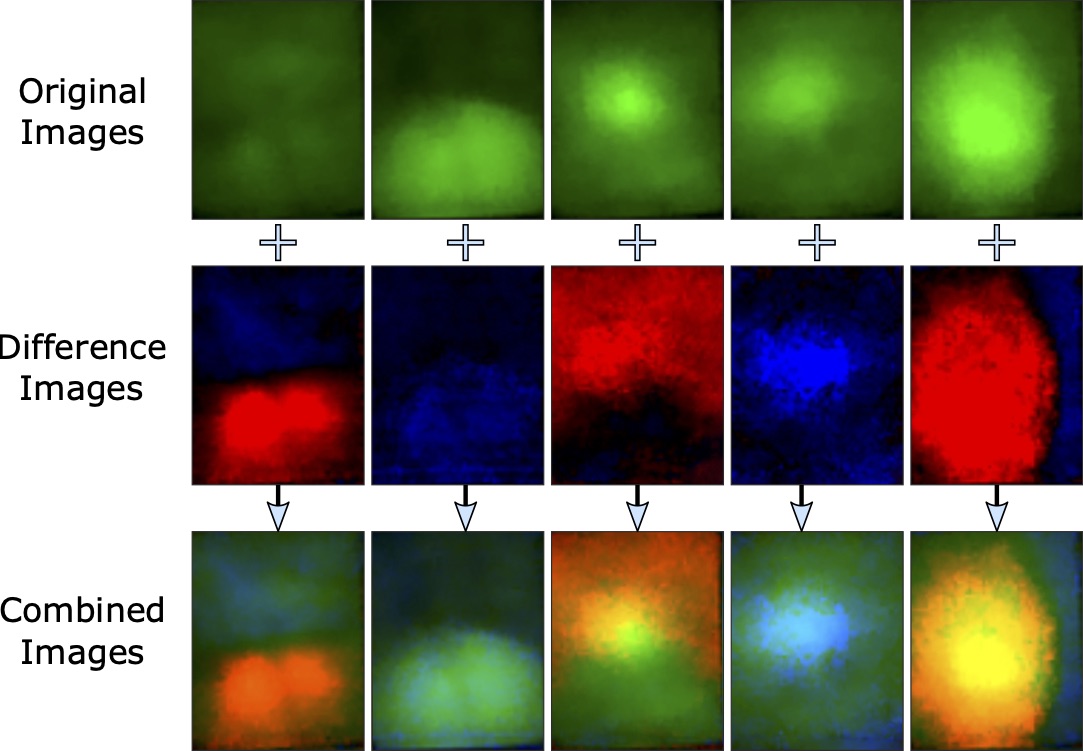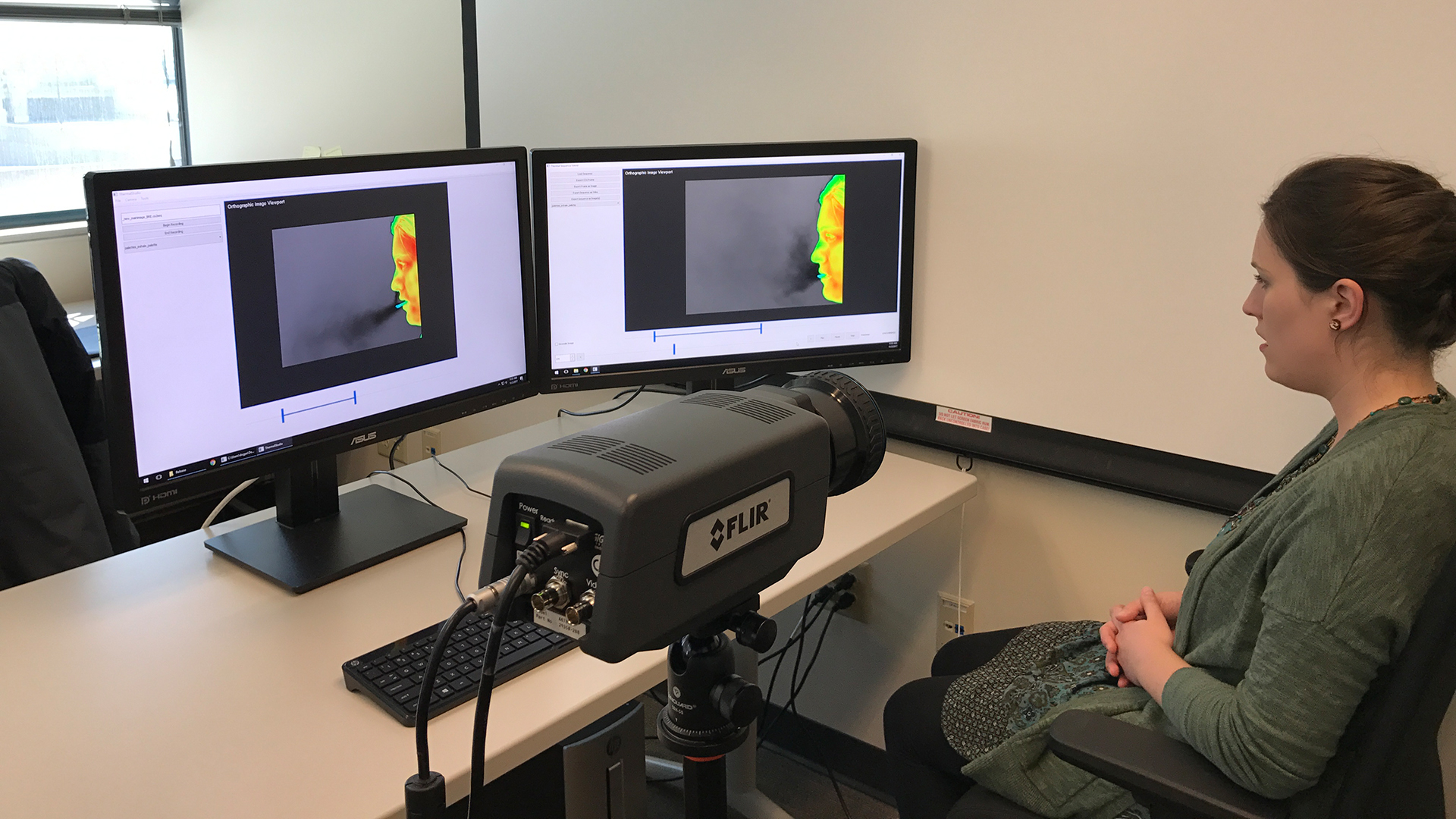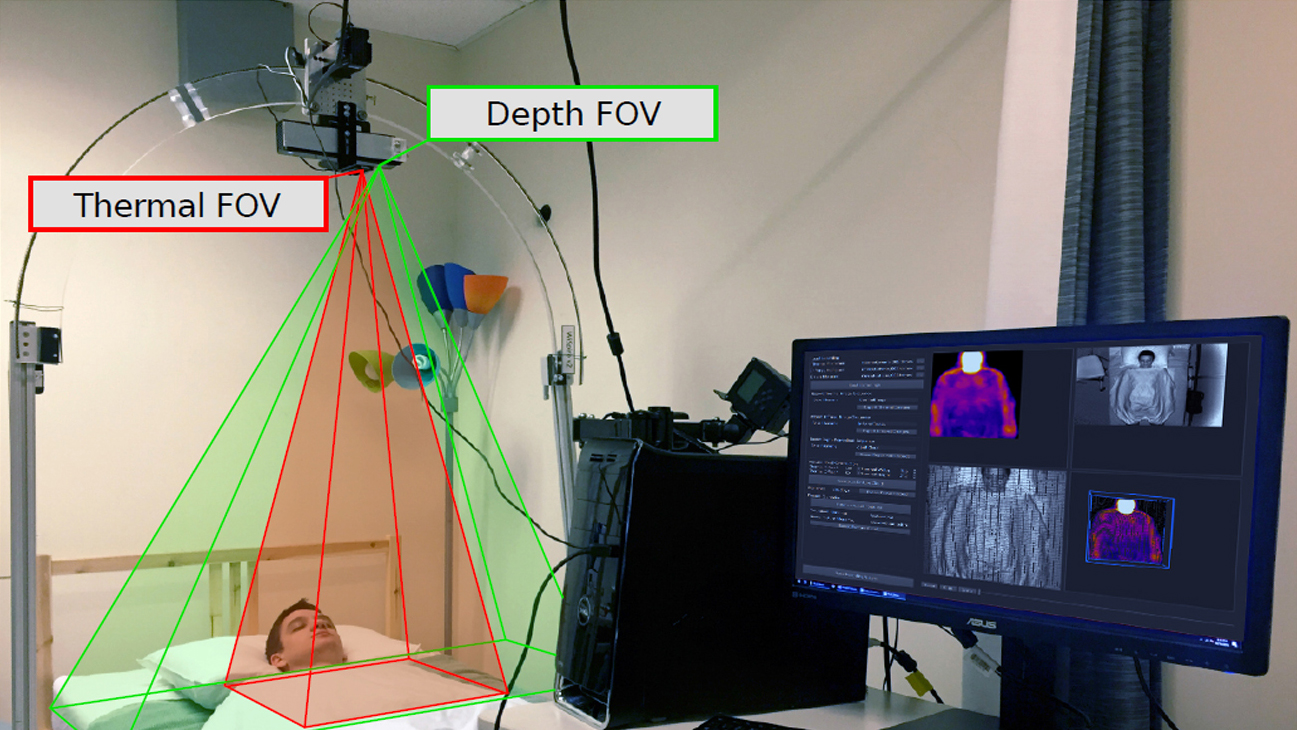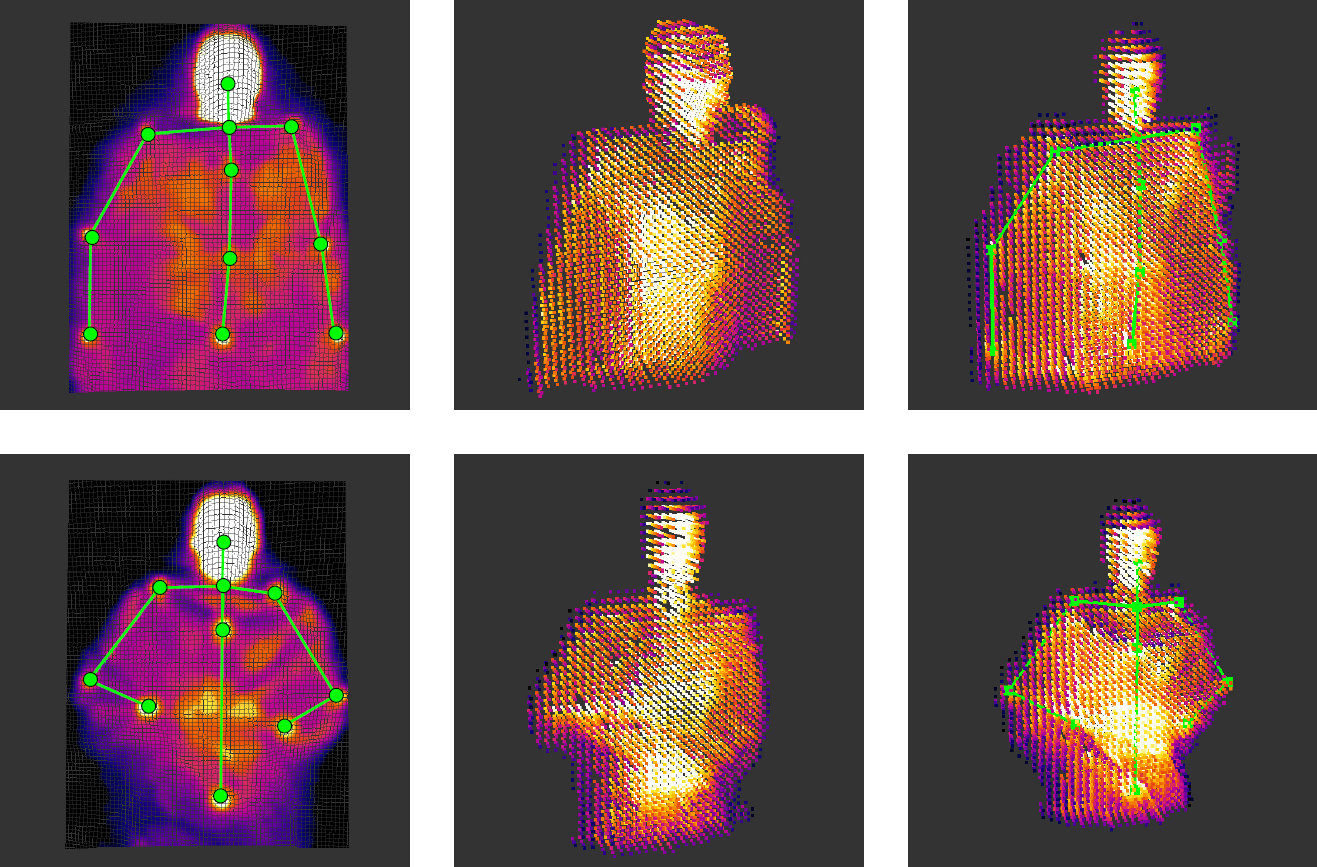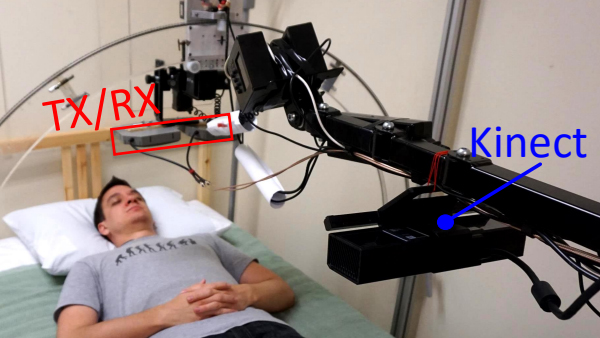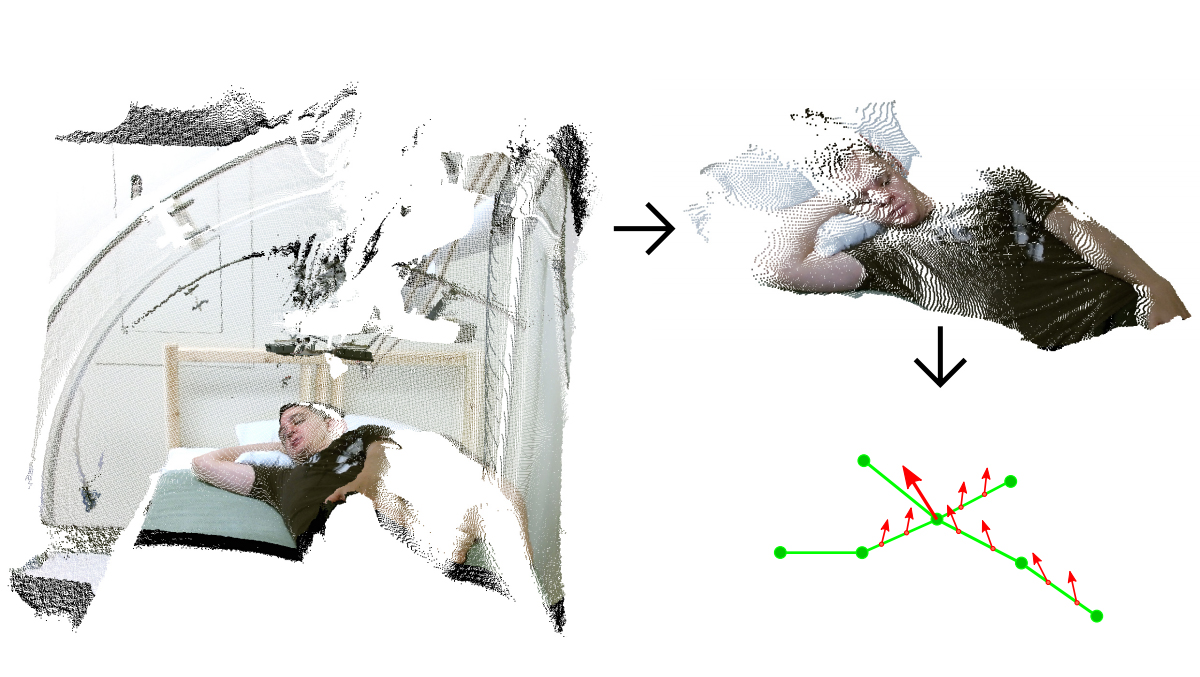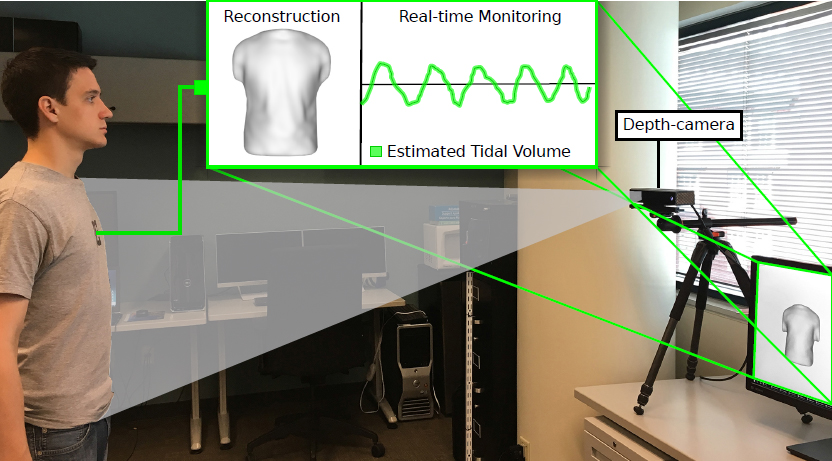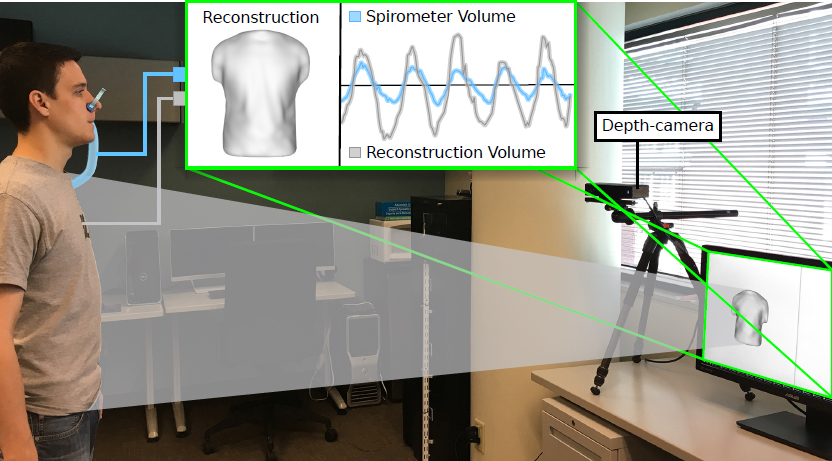
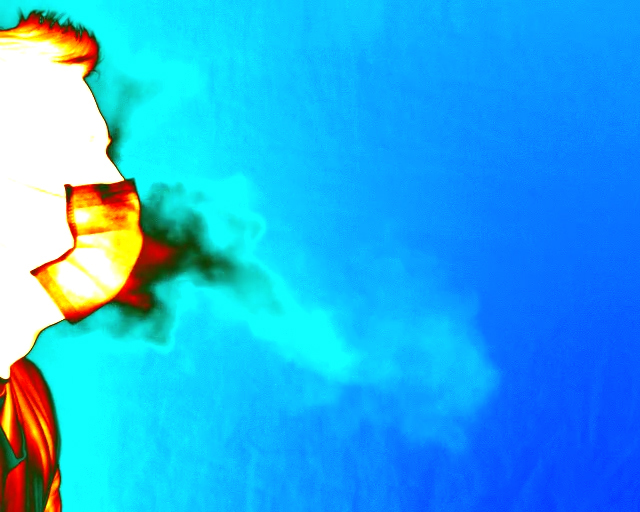
Description: Caregiver-patient interactions present a significant challenge in how healthcare can be delivered effectively and safely under the threat of highly-infectious diseases in the absence of solutions that guarantee protection to both caregivers and patients. These risks have recently become much more pronounced with the recent findings that suggest that the SARS-CoV-2 virus can now be spread through airborne transmission. This means that all individuals within these environments are all directly exposed to exhaled particulates, even with social distancing and Personal Protection Equipment (PPE) use. The societal implication of failing to reduce the risk to employers, caregivers, and their patients will have a profound impact on our ability to combat the COVID-19 threat. To address this problem, we propose to create a multi-modal airborne contagion mapping system that tracks exhaled particulates through visual exhale behaviors and identifies behaviors that contribute to higher transmission rates. Through this new form of analysis, we will be able to objectively evaluate social distancing protocols, PPE use, and create more effective risk mitigation strategies. These solutions can then be adopted into public health safety solutions for nursing homes, daycares, schools, and everyday workplaces including offices and retail stores.